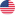
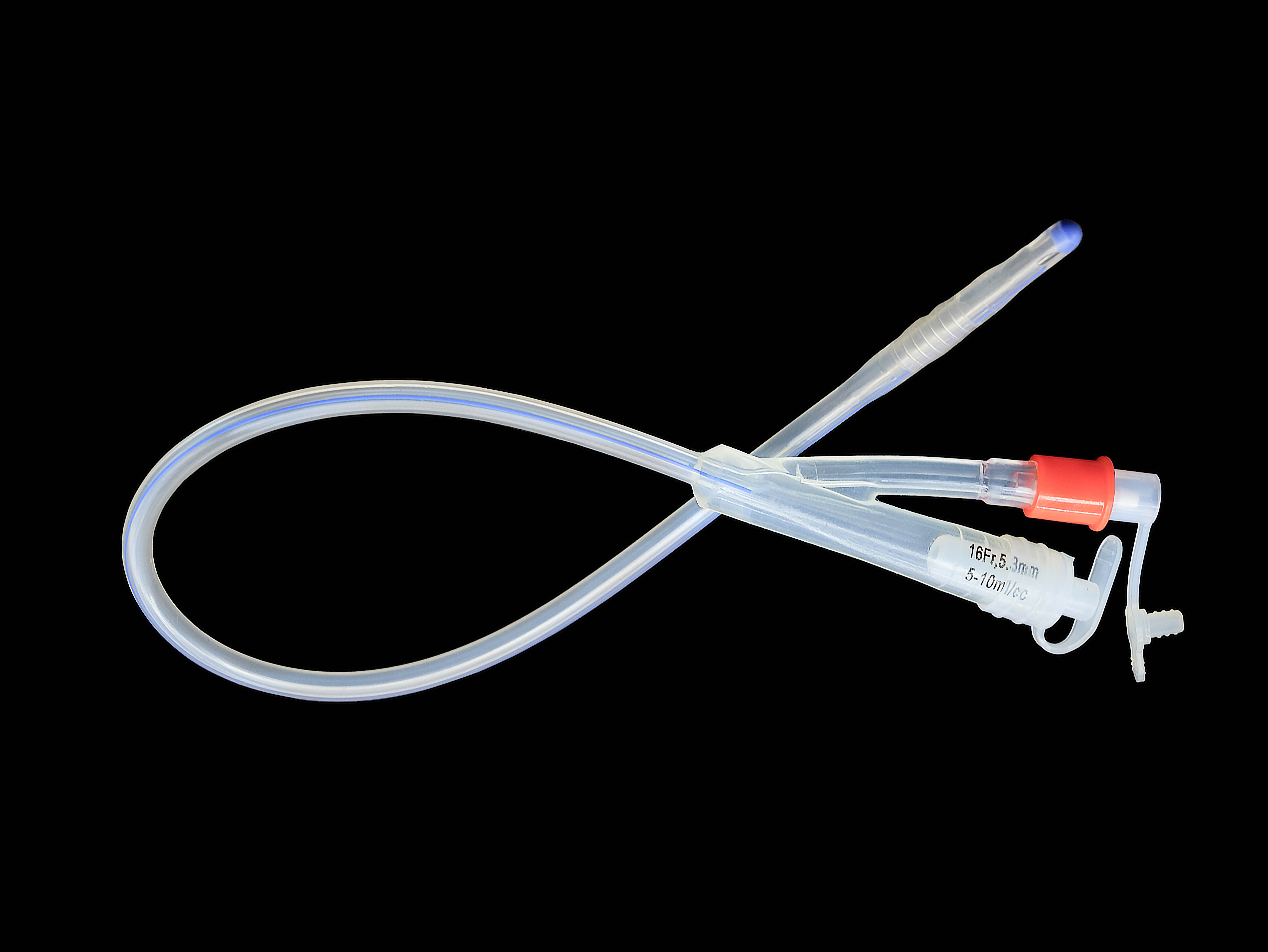
Briefly describe the characteristics of disposable silicone catheters
source:www.villmen.com | Release time:2025年06月05日1、 Material characteristics
1. Excellent biocompatibility
Using medical grade silicone material, it is harmless and non-toxic to human tissues, reducing the risk of urethral mucosal allergies or inflammation.
Soft and skin friendly, with minimal damage to the urethra during long-term retention, suitable for sensitive populations such as children and the elderly.
2. Strong corrosion resistance
Silicone has stable chemical properties and is not easily reacted with electrolytes, drugs, etc. in urine, which can maintain the performance of the catheter for a long time.
2、 Structural design features
1. The tube body is soft and has good elasticity
The texture is soft and bendable, reducing friction of the urethral mucosa during insertion, lowering patient discomfort and the risk of urethral injury.
Good elasticity, less likely to cause deformation or blockage of the catheter due to patient activity.
2. Multiple specifications selection
The diameter (such as F8-F24) and length are diverse, suitable for patients of different ages, genders, and clinical needs (such as children).
3. Balloon design is safe and reliable
The balloon (with a capacity of 5-30ml) can be fixed with water injection to prevent detachment and avoid damaging the bladder mucosa.
3、 Clinical application advantages
1. Disposable to reduce the risk of infection
To avoid cross infection caused by repeated use and comply with hospital infection control requirements.
2. Easy to operate
Smooth surface, low insertion resistance, and combined with lubricating gel can further improve the smoothness of operation.
3. High drainage efficiency
The lumen is unobstructed, and the lateral orifice design is reasonable to ensure smooth urine drainage and reduce sedimentation or blockage.
4、 Applicable scenarios
1. Short term indwelling: temporary drainage such as postoperative dysuria and urinary retention after anesthesia.
2. Long term retention: Patients with neurogenic bladder, urethral stricture, advanced tumors, etc. who require long-term catheterization.
3. Special population: People who are allergic to latex (silicone is a substitute for latex to avoid allergic reactions).
prev:
Which groups of people are suitable for using the…
next:
What is the principle of the circumcision stapler

 English
English
 18915600208
18915600208
 微信号:
微信号:


 Suzhou Weimeng Medical Equipment Co., Ltd
Suzhou Weimeng Medical Equipment Co., Ltd
 Our service hotline:0512-51316666,18915600208
Our service hotline:0512-51316666,18915600208
 Company address: Building 7, A3, No. 2 Jianye Road, Changfu Street, Changshu City, Jiangsu Province
Company address: Building 7, A3, No. 2 Jianye Road, Changfu Street, Changshu City, Jiangsu Province
 Contact email: ronghui@villmen.com
Contact email: ronghui@villmen.com
 WeChat
WeChat
 Contact
Contact
 Telephone
Telephone